Blockchain technology has emerged as one of the most transformative innovations of the 21st century, yet many people still struggle to understand what it actually is and why it matters. Today, we'll demystify blockchain technology, explore how it works, and examine why it's reshaping industries across the globe.
What is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a decentralised and distributed ledger that uses cryptography as a trust mechanism, enabling transparent information sharing without a central authority. Think of it as a digital record book that's simultaneously stored on thousands of computers worldwide, where every transaction is permanently recorded and verified by the network itself.
Traditional vs. Blockchain Systems
To understand blockchain's revolutionary nature, let's compare it to traditional systems:
Traditional System (Centralized):
- Single point of control (and failure)
- Trust required in the central authority
- Limited transparency - users must trust the system
- Potential for censorship or manipulation
Blockchain System (Decentralized):
- No single point of failure
- Trustless system - cryptography provides trust
- Complete transparency - all transactions visible
- Censorship resistant - no single authority can control it
How Does Blockchain Work?
Understanding blockchain requires grasping several interconnected concepts that work together to create this revolutionary system.
1. Blocks and Chains
Blocks are containers that hold a collection of transactions. Each block contains:
- Block Header: Metadata about the block
- Merkle Root: A hash representing all transactions in the block
- Previous Block Hash: Creates the "chain" linking blocks together
- Timestamp: When the block was created
- Nonce: A number used in the mining process
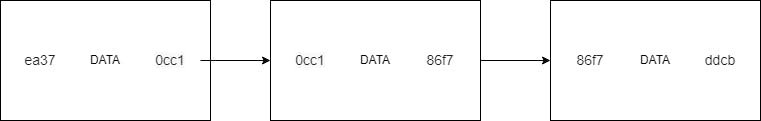
The Chain is formed by each block containing the hash of the previous block, creating an immutable sequence:
Blockchain immutability: each block contains the hash of the previous block. If someone tries to modify Block 1, its hash changes, which breaks the link to Block 2. This cascading effect makes historical tampering computationally infeasible.
2. Cryptographic Hashing
Blockchain uses SHA-256 hashing to create unique fingerprints for data. Key properties:
- Deterministic: Same input always produces same hash
- Fixed length: Always 256 bits regardless of input size
- Avalanche effect: Tiny input change completely changes output
- Irreversible: Cannot derive input from hash
Example:
3. Digital Signatures and Public Key Cryptography
Blockchain uses elliptic curve cryptography for digital signatures:
Key principles:
- Private key: Secret, used to sign transactions
- Public key: Shared, used to verify signatures
- Address: Derived from public key, like an account number
4. Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms ensure all network participants agree on the blockchain's state. Two primary types:
Proof-of-Work (PoW)
Used by Bitcoin, miners compete to solve computational puzzles:
Characteristics:
- Energy intensive but highly secure
- Decentralized - anyone can participate
- Predictable block times through difficulty adjustment
Proof-of-Work mining loop: miners repeatedly increment the nonce and hash the block until they find a hash meeting the difficulty target. This computational race secures the network through energy expenditure.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Used by Ethereum 2.0, validators are chosen based on their stake:
Advantages:
- Energy efficient (99% less energy than PoW)
- Faster finality - transactions confirmed quicker
- Economic security - validators lose stake for malicious behavior
Proof-of-Stake validator selection: validators with larger stakes have higher probability of being chosen. Valid blocks earn rewards, while malicious behavior results in stake slashing, creating economic incentives for honest participation.
Real-World Applications and Impact
1. Financial Services Revolution
Cryptocurrency Adoption
The numbers speak for themselves:
- 23,000+ cryptocurrencies currently exist
- $1+ trillion total market capitalization
- 100+ million people own cryptocurrency worldwide
- El Salvador adopted Bitcoin as legal tender
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi has recreated traditional financial services on blockchain:
DeFi Achievements:
- $100+ billion total value locked (TVL)
- 24/7 global access to financial services
- No traditional banking required
- Programmable money through smart contracts

2. Enterprise Adoption
Major corporations are integrating blockchain:
Supply Chain Management
Benefits:
- Food safety: Track contamination sources in seconds vs. days
- Authenticity: Verify product genuineness
- Efficiency: Reduce waste through better tracking
- Consumer trust: Transparent supply chains
Corporate Implementations:
- Walmart: Food traceability (reduced tracking time from days to seconds)
- De Beers: Diamond authenticity verification
- Maersk: Shipping container tracking
- JPMorgan: JPM Coin for institutional transfers
3. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Governments worldwide are exploring digital versions of their currencies:
CBDC Benefits:
- Financial inclusion for unbanked populations
- Reduced transaction costs for cross-border payments
- Monetary policy precision through programmable money
- Financial crime prevention through transaction tracking
The Economic Impact
Market Size and Growth
The blockchain industry represents massive economic potential:
Real Estate and Asset Tokenization
Benefits:
- Fractional ownership of expensive assets
- Global investment opportunities
- Increased liquidity for traditionally illiquid assets
- Reduced intermediary fees
Technical Challenges and Solutions
1. Scalability: The Blockchain Trilemma
Blockchain systems face a fundamental trilemma between:
- Decentralization: Maintaining distributed control
- Security: Ensuring network integrity
- Scalability: Processing many transactions quickly
Layer 1 Solutions (Base Layer):
Layer 2 Solutions (Built on Top):
- Lightning Network (Bitcoin): Payment channels for instant transactions
- Polygon (Ethereum): Sidechains with periodic settlement
- Arbitrum/Optimism (Ethereum): Optimistic rollups
2. Energy Consumption
Bitcoin's energy usage has sparked environmental concerns:
3. Regulatory Landscape
Governments worldwide are developing blockchain regulations:
Progressive Approaches:
- Switzerland: Crypto Valley with favorable regulations
- Singapore: Clear regulatory framework for crypto businesses
- Estonia: Digital residency and blockchain initiatives
Restrictive Approaches:
- China: Banned cryptocurrency trading and mining
- India: Considering cryptocurrency ban with exceptions
- Russia: Mixed signals on cryptocurrency adoption
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Emerging Trends and Technologies
1. Interoperability Protocols
Connecting different blockchain networks:
2. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
Preparing for quantum computing threats:
3. AI and Blockchain Integration
10-Year Blockchain Roadmap (2025-2035)
Getting Started: Your Blockchain Journey
For Developers
1. Learn the Fundamentals
2. Build Your First DApp
3. Essential Development Tools
- Hardhat/Foundry: Development environments
- MetaMask: Browser wallet for testing
- Remix: Online Solidity IDE
- The Graph: Indexing blockchain data
- IPFS: Decentralized storage
For Business Leaders
1. Identify Use Cases
2. Pilot Project Framework
- Define the Problem: What inefficiency does blockchain solve?
- Assess Blockchain Fit: Is decentralization necessary?
- Choose the Right Platform: Ethereum, Hyperledger, or custom?
- Start Small: Proof of concept before full deployment
- Measure Impact: ROI, efficiency gains, user adoption
For Investors
1. Investment Categories
2. Risk Assessment Framework
- Technology Risk: Is the blockchain solution mature?
- Regulatory Risk: What's the regulatory environment?
- Market Risk: How volatile is the asset?
- Liquidity Risk: Can you exit positions easily?
- Security Risk: Has the protocol been audited?
Conclusion: The Blockchain Revolution
Blockchain technology represents more than just a technological innovation—it's a paradigm shift toward decentralized, transparent, and trustless systems. As we've explored throughout this comprehensive guide, blockchain's impact extends far beyond cryptocurrency into supply chains, finance, healthcare, governance, and countless other domains.
Key Takeaways:
1. Technological Foundation
- Blockchain combines cryptography, consensus mechanisms, and distributed systems
- It solves the double-spending problem without central authorities
- Smart contracts enable programmable, autonomous agreements
2. Real-World Impact
- $163+ billion projected market by 2029
- 23,000+ cryptocurrencies demonstrating diverse applications
- Major corporations like Walmart, JPMorgan, and others actively implementing blockchain
3. Future Potential
- CBDCs will reshape monetary systems
- DeFi is recreating financial services
- NFTs and tokenization are creating new asset classes
- Web3 promises a more decentralized internet
4. Challenges Being Addressed
- Scalability solutions through Layer 2 and sharding
- Energy efficiency via Proof-of-Stake consensus
- Regulatory clarity emerging globally
- User experience improvements making blockchain accessible
The Path Forward
Whether you're a developer looking to build the next generation of applications, a business leader exploring blockchain solutions, or an investor seeking opportunities in this space, the key is to start learning and experimenting now.
The blockchain revolution is not a distant future—it's happening today. Major institutions are adopting blockchain, governments are launching digital currencies, and entire industries are being transformed.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain technology embodies the principles of decentralization, transparency, and empowerment. It promises a future where:
- Individuals control their data and assets
- Intermediaries become optional, not mandatory
- Global collaboration happens without borders
- Innovation accelerates through open protocols
As Nick Szabo envisioned decades ago, we're building systems that are autonomous and transparent—smart contracts and blockchains that can operate independently while providing complete visibility into their operations.
The question isn't whether blockchain will reshape our world—it already is. The question is: Will you be part of building that future?
The blockchain space evolves rapidly. Stay informed, keep learning, and remember that today's experiments may become tomorrow's standards. The decentralized future is being built one block at a time.
Resources for Continued Learning
- Technical: Ethereum Documentation, Bitcoin Whitepaper
- Educational: MIT OpenCourseWare Blockchain, Coursera Blockchain Courses
- Development: Solidity Documentation, Web3 Development Stack
- News: CoinDesk, The Block, Decrypt
Reviewed by Arthur Costa - Senior Full-Stack Engineer & Tech Lead